2022 Research
January
Tremors can be described as an involuntary and uncontrollable movement of parts of the body. They are classified based on characteristics like frequency, amplitude, activation, among others. Such parameters are essential to identify so that better treatment can be provided to patients suffering from tremor conditions. Electromyography (EMG) is a diagnostic procedure to assess the health of muscles and motor neurons. Though used in the past, EMG is expensive, invasive, and potentially painful. Therefore, there is the need to create a painless, affordable, fast, and effective apparatus that can gather, quantify, and classify tremor parameters from patients, resulting in a short list of possible diagnoses which can be narrowed down by a physician. This research aims to create a Tremor Diagnosis Device (TDD) using an accelerometer, Raspberry Pi 4, and Python code.
February
Lung cancer is the cancer that has claimed the most lives worldwide for decades. Specifically, small cell lung cancer has been difficult to treat due to its ability to rapidly adapt and resist to treatment. In this study, public datasets of small cell lung cancer cells that became resistant after treatment with talazoparib or prexasertib were analyzed using bioinformatic tools to elucidate common processes that allow for treatment refraction. The reactive oxygen species (ROS) pathway and TGF-beta signaling pathway were prominent in the tissues treated with both treatment types. Shared genes contributing to these pathways in both treatments were studied for their role in the development of resistance. Seven genes were identified that should be further tested as potential targets to reverse treatment resistance.
March
Brain tumours are challenging to treat, partly because the blood-brain barrier (BBB) hinders targeted drug treatment. Patients diagnosed with aggressive brain tumours like glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) present low median survival of 15 months despite surgery with concurrent chemotherapy and radiotherapy. The poor prognosis and limited therapeutic effect have led to the exploration for an alternative intervention: nanotechnology. This paper focuses on nanotechnology-based diagnostic tools and drug delivery systems, such as multifunctioning nanoparticles that comprise an anti-cancer drug, an imaging agent and tumour specific ligands, which enhances diagnostic sensitivity and therapeutic efficacy against the malignant cells.
Green fluorescent protein (GFP), a fluorescent marker extracted from Aequorea victoria, has been a prominent tool for protein visualisation in modern biomedical research. When properly folded, it emits green fluorescence upon UV illumination. Increased understanding regarding GFP’s structure, maturation, and spectrochemical properties allows its optimisation, development of variants such as split-GFP, and protein research applications. Understanding protein localisations and protein-protein interactions can provide insights into the functions of the proteome.
April
This paper focuses on processes of formation and weighing of supermassive black holes, and how they can be located via the Citizen Science Project ‘RADIO GALAXY ZOO: LOFAR’ presented by Zooniverse. Thousands of jets and galaxies have been seen by the Low Frequency Analyzer and Recorder (LOFAR) survey, and an automatic "source finder" computer programme has identified them. This programme is not without flaws, and it occasionally separates a single radio source into numerous components. Through this project, radio astronomers require assistance in reassembling the components that the source finder programme mistakenly separated. This will allow the recreation of the entire radio source from its constituent parts.
May
As COVID-19 uproots millions of lives globally, it is crucial to understand the virus’s transmission routes. One such route, aerosol transmission, has been largely ignored by global health leaders until recently, despite surmounting evidence supporting its prevalence. Aerosols (droplet nuclei <5 in diameter) are produced during routine respiratory functions, can remain suspended in the air over prolonged and distances and can carry infectious SARS-CoV-2 particles. Thus, it is imperative that universities implement solutions to prevent SARS-CoV-2 aerosol transmission in spaces at risk for infectious aerosol buildup, namely enclosed, high-occupancy spaces. This paper investigates the dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 aerosol transmission and identifies the best practices that institutions should follow to minimize classroom aerosol transmission.
June
Sports have always been a part of humans’ lives, with the most talked about event this summer being the Olympics, originally dating back roughly 3000 years ago. Physics on the other hand, has also been studied since the times of Aristotle. Both disciplines were rather disjoint and uncorrelated, however, fast forward to modern day physics and the increasingly competitive nature in sports, the two disciplines have found a way to merge into a new field of sports sciences. With current fast-paced development in science and technology, research within the field of sport sciences has mushroomed, which has led to some controversy due to beliefs that physics has overstayed its welcome in sports, causing athletes to overachieve unfairly. The main question in hand is to where the line should be drawn at the application of physics in sports to still be considered a “fair” game?
July
Rodent body weight data from National Toxicology Program studies is an important end point used to determine if a toxicant causes adverse effects. Statistical tests for differences between body weights of control and treated groups often assume that the data are normally distributed (i.e., are bell-shaped curves). This study evaluated the importance of the normality assumption in statistical testing of rodent body weight measurements. It was found that the normality test used in this project, Shapiro-Wilk’s test for normality, has 6-56% power to detect skew normal distributions with samples sizes of 50 animals or less. However, statistical tests that compare body weights in a control group to a treated group were able to detect 10% differences in body weight with at least 80% power for sample sizes of 10, 20, and 50 rodents for both normally distributed data and data with a skew normal distribution while keeping False Positive Rates at an acceptable level of approximately 5%.
August
On the African continent, Amaranth is one of the most widely grown and consumed indigenous crops. The genus Amaranth is one of the most grown leaf vegetables, cereals or decorative plants. Weather factors, the environment, genotype and production practice all influence Amaranth’s vegetative development. Most farmed Amaranth cultivars have low leaf and grain yields, owing to a paucity of good variations. Grain Amaranth growth can be enhanced with the use of suitable cultivars.
September
A part of the United States’ healthcare system, safety-net systems deliver a significant amount of care to members of vulnerable populations. These populations often face unique challenges in accessing healthcare due to lack of insurance, limited income and marginalization by their race, ethnicity and gender identity. This study aims to understand how these individuals perceive their healthcare support within the current safety-net framework. A qualitative analysis was performed on a single questionnaire item that asked participants to openly state a belief or opinion regarding how safety-net systems in Washington, D.C. and Washington State could better support their healthcare needs. Our findings imply that even with access to healthcare through the safety-net system, patients from low-resourced populations, particularly those who identify as transgender, continue to face significant barriers to achieving adequate healthcare resources and support that could impact health outcomes.
October
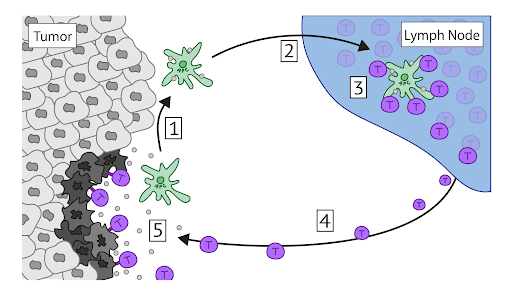
Monocytes and macrophages are two developmentally related immune cell types that can infiltrate tumors of cancer patients. These cells critically impact cancer progression due to their abilities to both induce and suppress the body’s natural anti-cancer immune response. Since these cell types can directly hinder the efficacy of immunotherapy treatments, identifying strategies to inactivate and inhibit their functions is of great therapeutic interest. In this review, we discuss how monocyte and macrophage populations contribute to the cancer immunity cycle, a cycle which specifically targets cancer cells while keeping healthy cells unharmed. Specifically, our review focuses on the roles of these cells in the blood (circulating monocytes), tumor tissue (tumor-resident macrophages and monocyte-derived dendritic cells), as well as lymph nodes (lymph node-resident macrophages). We discuss how these cells can promote cancer growth and can participate in the immune attack against cancer through the secretion of cytokines, thereby aiding or harming the immune response. We highlight how certain migrating macrophage populations can take up tumor antigens and travel to the lymph node to activate T cells to begin the killing of tumor cells—a role that is usually thought to be fulfilled by only dendritic cells. Lastly, this review highlights why monocytes and macrophages are promising targets for treating cancer, and how these cells can be reprogrammed to improve patient responses to existing therapies, termed immunotherapies, that act to enhance the body’s natural anti-cancer defenses.
November
Previous investigations have indicated potential associations between dedicated quarantine and depression. However, a literature gap exists regarding the impact of home quarantine on mental status. Accordingly, our study aims to estimate the psychological effect of home quarantine on university students in Iraq, Jordan and Syria. Our study was conducted via an online survey of 4955 randomly selected university students from 123 universities in Iraq, Jordan and Syria. Our survey included questions regarding sociodemographic characteristics along with the validated Arabic version of the CES-D (The Centre for Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale) to assess the risk and prevalence of depressive symptoms. Among respondents, 73.2% were women, 89.9% were aged between 17 and 24 years and 65.5% were studying medical specialties. The mean CES-D score was 25.57 ± 12.6. The CES-D score was greater than 16 for 75.8% of quarantined persons, a typically recommended cut-off to identify patients at risk of clinical depression. Risk factors for depression were studying in Iraq, being female, being of a younger age, smoking, having a low and middle income, partial adherence to home quarantine rules and living alone or with a person taking immunosuppressants (p < .05). A high prevalence of clinical depression was observed among university students during the COVID-19 home quarantine. The evidence from this study suggests that post-quarantine psychological interventions are needed; governments should focus on providing psychological services to those in need in the aftermath of the COVID-19 pandemic and addressing psychological aspects while preparing for future pandemics.
December
In the current COVID-19 pandemic, various Automated Exposure Notification (AEN) systems have been proposed to help quickly identify potential contacts of infected individuals. All these systems try to leverage the current understanding of the following factors: transmission risk, technology to address risk modeling, system policies and privacy considerations. While AEN holds promise for mitigating the spread of COVID-19, using short-range communication channels (Bluetooth) in smartphones to detect close individual contacts may be inaccurate for modeling and informing transmission risk. This work finds that the current close contact definitions may be inadequate to reduce viral spread using AEN technology. Consequently, relying on distance measurements from Bluetooth Low-Energy may not be optimal for determining risks of exposure and protecting privacy. This paper’s literature analysis suggests that AEN may perform better by using broadly accessible technologies to sense the respiratory activity, mask status, or environment of participants. Moreover, the paper remains cognizant that smartphone sensors can leak private information and thus recommends additional objectives for maintaining user privacy without compromising utility for population health. This literature review and analysis will simultaneously interest (i) health professionals who desire a fundamental understanding of the design and utility of AEN systems and (ii) technologists interested in understanding their epidemiological basis in the light of recent research. Ultimately, the two disparate communities need to understand each other to assess the value of AEN systems in mitigating viral spread, whether for the COVID-19 pandemic or for future ones.